**Title:** How CoinJoin Anonymity Can Be Compromised by Clustering
**Meta Description:** Explore how clustering can undermine CoinJoin’s anonymity and the implications for privacy in cryptocurrency transactions.
**URL Slug:** coinjoin-anonymity-clustering
**Headline:** Understanding the Vulnerabilities of CoinJoin Anonymity Through Clustering Techniques
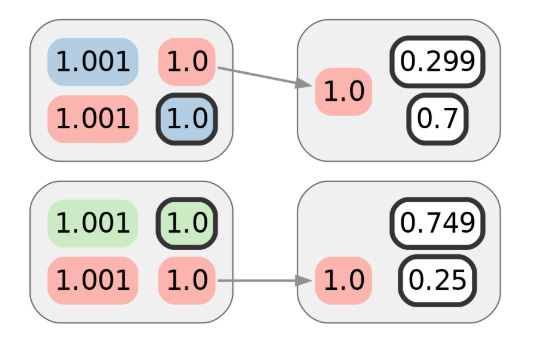
In the realm of cryptocurrency, achieving anonymity is a primary objective for many users seeking privacy in their transactions. However, the process of de-anonymization can be likened to a strategic game where an adversary attempts to identify individuals involved in specific activities within the system. This adversary has access to certain information and aims to deduce who among a group of candidates is responsible for a particular event. To thwart this adversary, it is essential to keep them guessing, which can be accomplished by either restricting their access to information or introducing randomness to complicate their efforts.
A familiar analogy can be drawn from the game “Guess Who?”, which is a turn-based variation of the broader game “twenty questions.” In “twenty questions,” a player selects an item from a defined set, and the opponent tries to identify it by asking up to 20 yes-or-no questions. In contrast, “Guess Who?” involves both players taking turns to guess the identity of a character from a fixed set of 24 cartoon figures, each with distinct features like hair color or style. Each character is uniquely identifiable by name.
The responses to yes-or-no questions can be represented as binary bits—zero or one. With 20 bits, one can represent any whole number from 0 to 1,048,575, which corresponds to 2²⁰-1. If a set is completely ordered, each element can be indexed by its position, allowing for unique identification. Thus, 20 bits can pinpoint one of over a million elements. However, in practical scenarios, the information derived from 20 answers is often less than optimal. Real-world sets and question combinations rarely align perfectly, and not every question will independently bisect the candidate elements.
For instance, consider a question like, “Does your character wear glasses?” versus a more strategic question such as, “Alphabetically, does your character’s name come before [the median remaining character’s name]?” The latter employs a binary search method, maximizing the informativeness of each answer. By continually halving the remaining candidates, this approach accelerates the identification process, requiring only a logarithmic number of steps compared to a linear search method.
In summary, while CoinJoin offers a layer of anonymity for cryptocurrency transactions, its effectiveness can be significantly compromised through clustering techniques. Understanding these vulnerabilities is crucial for users who prioritize privacy in their digital financial activities.
**FAQ Section:**
**Q: How does clustering affect the anonymity of CoinJoin transactions?**
A: Clustering can link multiple transactions to a single user, making it easier for adversaries to de-anonymize participants in CoinJoin transactions by analyzing patterns and connections.